
Resta Creme Moisturizer for Dry, Irritated Skin
Resta Crème provides superior lubricating and moisturizing protection for your skin. It “melts” on contact, penetrating skin cell layers and holding in moisture for 12
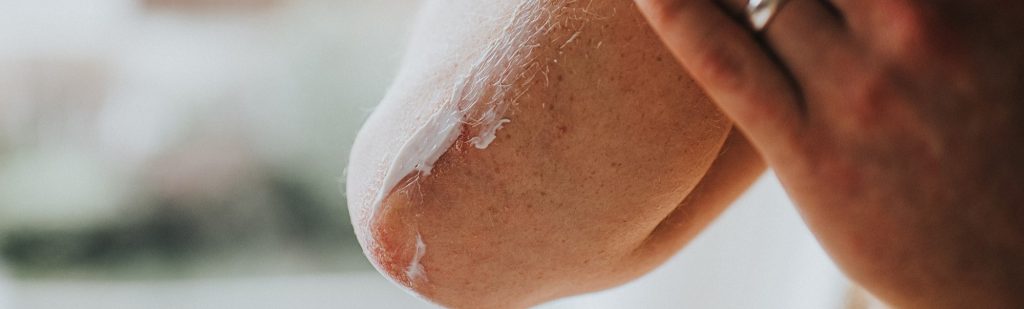
Eczema is often linked to an immune system response to a trigger. It involves a complex interplay of factors that include genetics, where individuals with a family history of eczema or allergies are more prone to develop the condition.
Environmental elements such as pollens, animal dander, and dust mites can initiate an inflammatory process in the skin. Skincare products or detergents containing irritants and chemicals can cause reactions in sensitive individuals. Stress is also recognized as a trigger that can exacerbate symptoms (source).
Untreated eczema can lead to several complications in affected individuals. Here’s what might happen:
To prevent these complications, treatment options should be explored, ranging from over-the-counter eczema creams to prescription medication. These treatments aim to reduce symptoms, improve the skin barrier function, and prevent infections and flare-ups.
It’s also important for individuals with eczema to consult with a healthcare provider to develop a tailored treatment plan.
Managing eczema typically involves a combination of skin care strategies and lifestyle adjustments. Selecting the right cream for eczema is a crucial step towards soothing the skin and managing symptoms.
Eczema is a common condition in infants, with about 10% to 20% experiencing it. Interestingly, nearly half of the infants diagnosed with eczema see either a complete resolution or significant improvement in the condition as they grow older (source). The occurrence of eczema, particularly atopic dermatitis, is often observed in the early stages of a child’s life, typically within the first six months. This prevalence is partly due to the increased sensitivity of a baby’s skin during their first year.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, it is noted that the majority of baby eczema cases resolve by the time children begin school, around ages 4 or 5. Additionally, as children move towards adolescence and adulthood, the severity of eczema tends to decrease. While some children may outgrow the condition entirely, others might continue to have sensitive skin or occasional flare-ups of symptoms throughout their lives.
Creams are generally lighter, absorb quickly, and are suitable for moderate eczema. They are often preferred for daily use in large areas of the body. Ointments, on the other hand, are thicker and might be more appropriate for localized and severe dry patches, as they provide a stronger barrier and more intense moisture.
For targeted treatment, eczema creams such as Eucerin Original Healing Cream – Extremely Dry, Compromised Skin, and Sween 24 Once A Day Cream are often recommended by dermatologists for their gentle formulations that support skin healing. These products typically contain ingredients to help restore the skin barrier and retain moisture.
Choosing the right eczema cream may involve some trial and error, as different skin types respond to ingredients in various ways. Consulting with a dermatologist can also guide individuals toward a cream that is best suited to their specific condition.
With careful selection, the right cream can provide significant relief, helping to soothe the skin, reduce inflammation, and improve the quality of life for those dealing with eczema.

Resta Crème provides superior lubricating and moisturizing protection for your skin. It “melts” on contact, penetrating skin cell layers and holding in moisture for 12

Eucerin Original Healing Cream is a time-tested formula that helps heal and protect extremely dry, sensitive, and compromised skin. The thick, rich, formula provides intensive

Eucerin Original Healing Rich Creme
Heal very dry, sensitive skin with a creme uniquely formulated to repair and protect.
This emollient-rich formula, free of fragrances and
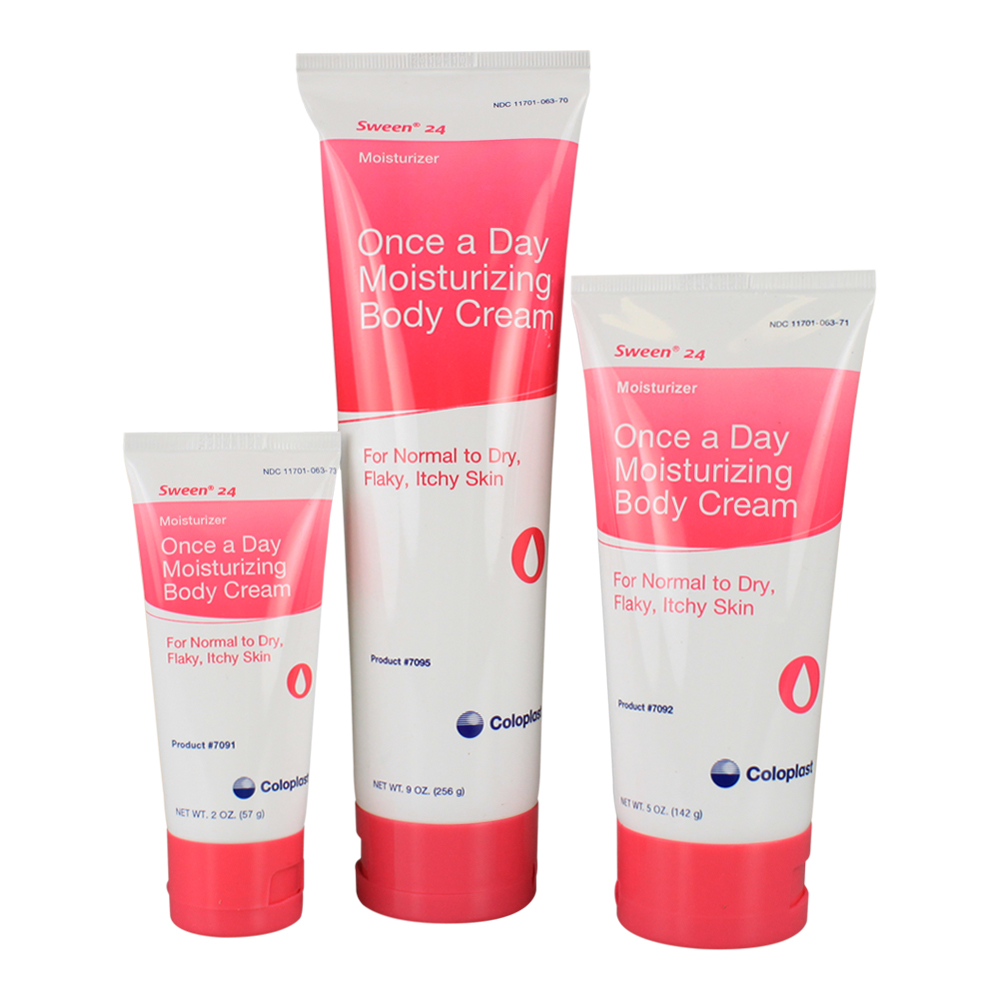

Sween 24 is a moisturizing cream formulated with dimethicone to soothe dry, chapped or chafed skin and lips for up to 24 hours. As both

If you’re living with dry skin, standard moisturizers and skin care products might not be

If you or someone close to you suffers from eczema, you know how frustrating it
Are you dealing with irritated skin? It could be sensitive, red, or dry – or

