
BARDIA Silicone Elastomer Coated 2-Way Foley
![]() Bard Medical Bardia Silicone-Elastomer Coated 2-Way Foley Catheter 5cc Balloon Capacity, Hydrophobic, Two Opposing Eye, Sterile. This catheter is made from
Bard Medical Bardia Silicone-Elastomer Coated 2-Way Foley Catheter 5cc Balloon Capacity, Hydrophobic, Two Opposing Eye, Sterile. This catheter is made from

Urinary retention affects both men and women, but it is more common in men as they get older. According to the National Institute of Health, about 1 in 10 men over 70 will develop some form of urinary retention in the next five years, and nearly 1 in 3 men over the age of 80 will experience this condition.
Below, we’ll break down the common symptoms of urinary retention, how to manage this condition, home treatments, and how it differs from other urology-related conditions.
Urinary retention occurs when the bladder doesn’t empty completely. This condition can be acute or chronic. It can affect anyone but is more common in men and older adults in general.
People who experience urinary retention often have a difficult time starting urination, a weak flow, or the feeling that their bladder is never fully empty. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to contact a medical provider for a proper diagnosis and a comprehensive care plan.
Common causes of urinary retention include obstructions, infections, and nerve issues. Obstructions can be caused by blockages like kidney stones or an enlarged prostate. Infections, including urinary tract infections (UTIs), can cause swelling, leading to urinary retention. Issues with the nerves that control bladder function also cause this condition.
Symptoms can differ from each individual. However, some of the most prominent symptoms of urinary retention include:
If you are experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to check in with a medical professional. Doctors can often provide diagnosis through physical exams, imaging tests, and/or urine tests.
Urinary retention is dangerous and can be life-threatening in some circumstances. If you are not able to urinate and/or notice pain in your abdomen, then you should seek medical assistance right away, as it could potentially be a sign of acute urinary retention. You should also talk with a healthcare professional if you notice any of the aforementioned symptoms in the previous section, which could be signs of chronic urinary retention.
Yes, constipation can cause urinary retention. If there are large amounts of stool in the colon, this could put pressure on the bladder. In turn, the bladder may not fill properly or be restricted when emptying, causing urinary retention.
There is such a thing as drug-induced urinary retention. This especially holds true for older patients who may already have a higher risk of developing urinary retention. According to the Cleveland Clinic, these drugs include the following:
Other drugs, such as blood pressure medications and muscle relaxants, can change how the muscles around your bladder work and cause symptoms.
There are several ways to improve your symptoms related to urinary retention. Some include preventative care, while others require medications, catheters, and further measures under the care of medical professionals.
There are several lifestyle changes that could improve your symptoms. This includes:
If those home treatment options aren’t bringing about signs of improvement, then there are other urinary retention treatment options to try. Be sure to consult your doctor for a personalized care plan for your unique situation. Some other treatment options may include:
Both urinary retention and incontinence deal with urination, but they are different conditions with entirely separate groups of symptoms. Urinary retention revolves around the difficulty of urinating and can result in the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. Incontinence deals with the involuntary leakage of urine. This is when sudden accidents happen because (small or large) a person cannot control their bladder function.

![]() Bard Medical Bardia Silicone-Elastomer Coated 2-Way Foley Catheter 5cc Balloon Capacity, Hydrophobic, Two Opposing Eye, Sterile. This catheter is made from
Bard Medical Bardia Silicone-Elastomer Coated 2-Way Foley Catheter 5cc Balloon Capacity, Hydrophobic, Two Opposing Eye, Sterile. This catheter is made from
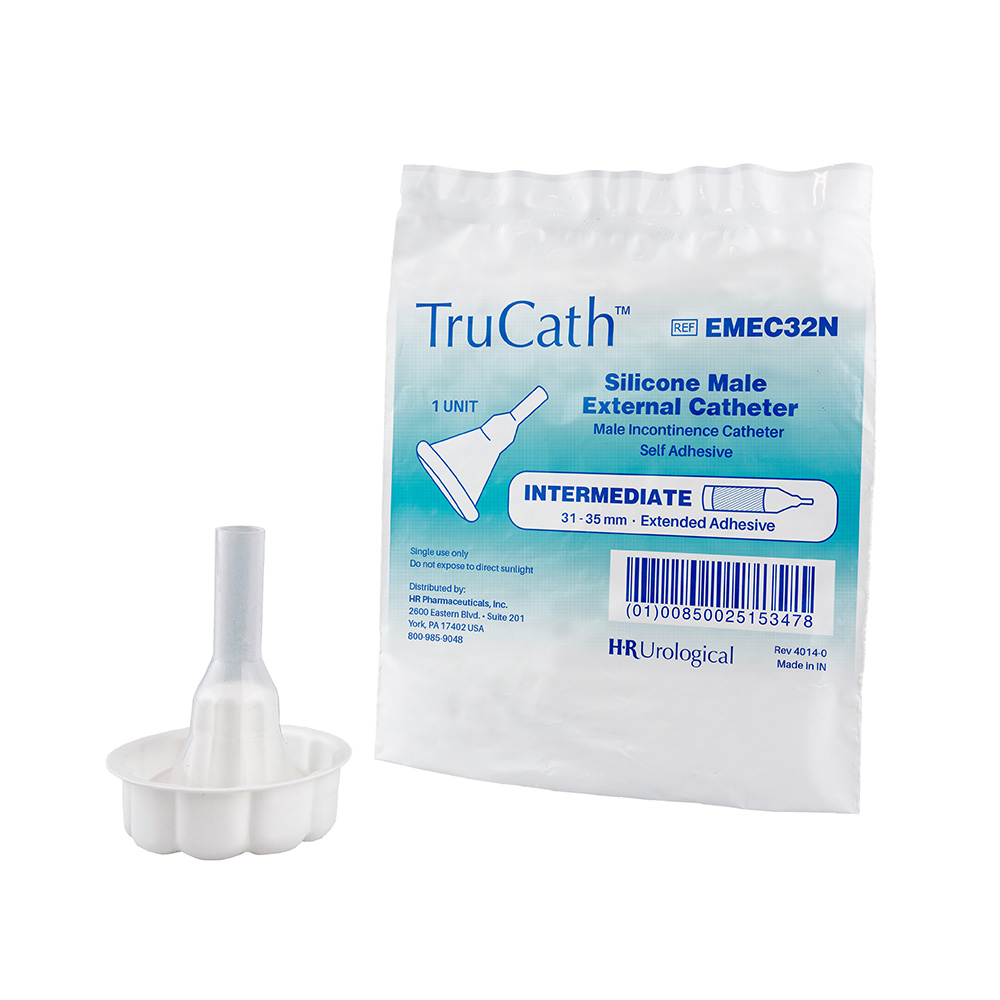
TruCath Male External Catheter with Extended Adhesive
TruCath Silicone Male External Catheters are designed to manage incontinence in a discreet, reliable, and easy-to-use way without the fear of leaks. Simply
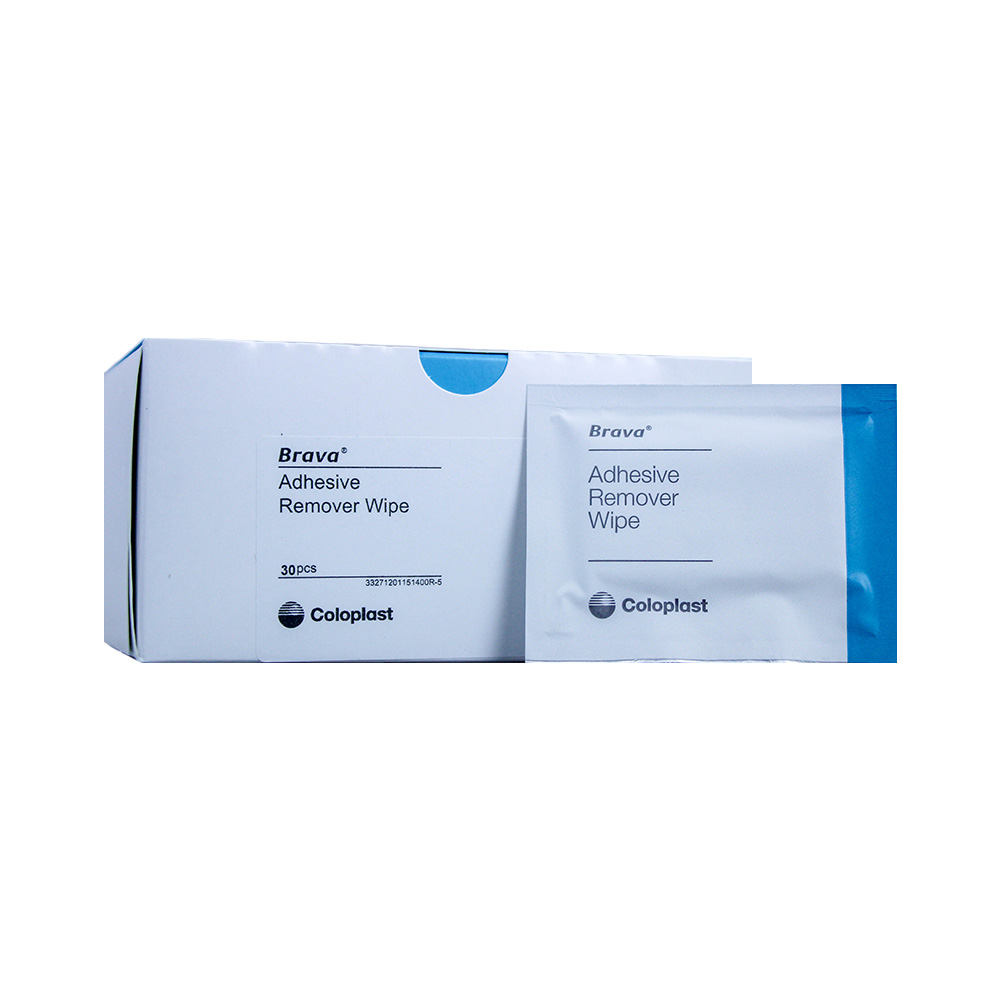
Free of alcohol, Brava Adhesive Remover Wipes offer a convenient, gentle solution for removing your ostomy system’s barrier wafer and ensuring the peristomal skin remains intact.
Benefits of Brava Adhesive

![]()
Featuring a protective dry sleeve, the SpeediCath® Flex Coudé Pro is a new flexible catheterization system for men living with
Urinary catheters are devices that help people urinate when they are unable to do so

Incontinence is a medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide, significantly impacting their quality

How do you keep fresh with incontinence? Here are some helpful tips from Medical Monks
